Lesson 29 - Embedding HTML content
Sometimes we want to embed HTML content on the canvas, such as a YouTube player, a CodeSandbox component, ShaderToy, and so on.
Create an HTML Container
Excalidraw does not support embedding HTML content on the canvas, but tldraw supports TLEmbedShape. It displays an HTML container (with an iframe or other elements) alongside or overlaid on the canvas <svg> element in the page, instead of being “fully” inside a single canvas.
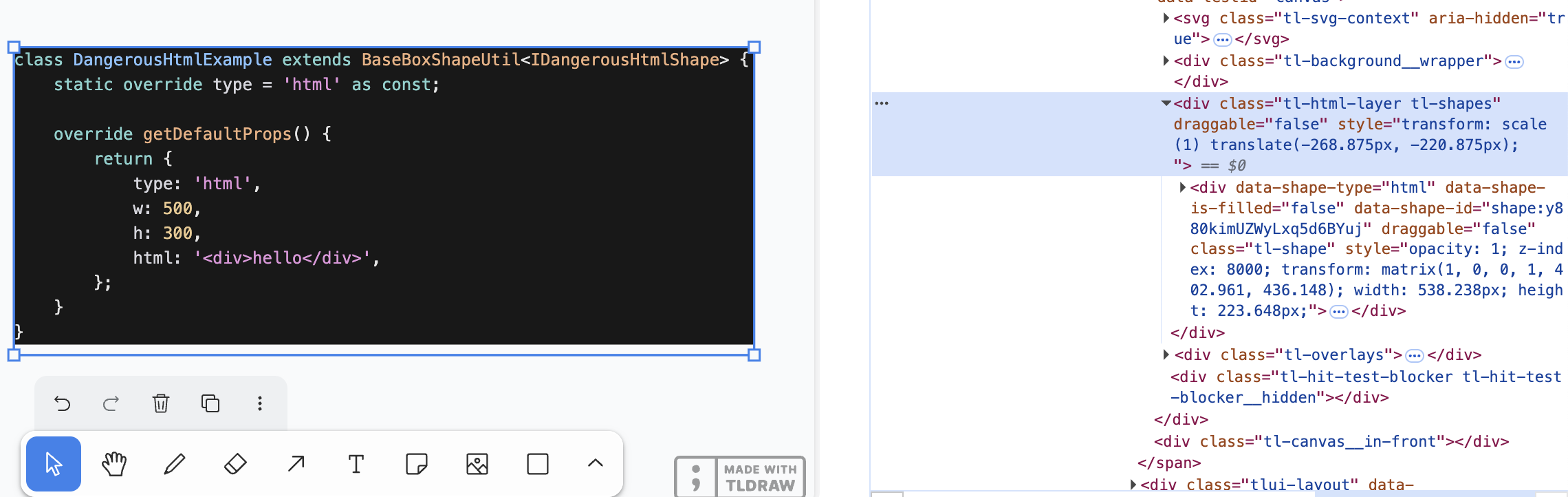
The container is divided into two layers:
- The HTML layer exists alongside the
<canvas>as its sibling node, containing all HTML containers and handling camera synchronization. - The HTML container serves as the container for each
html/embedshape and handles positioning for individual shapes.
Camera synchronization
In Lesson 4 - Camera, we introduced a series of important camera parameters: translation, rotation, and zoom. Now we need to map the camera parameters to the HTML container's CSS transform so the canvas and HTML container stay in sync.
const { cameraZoom, cameraX, cameraY } = this.appStateProvider.value;
$htmlLayer.style.transform = `scale(${toDomPrecision(
cameraZoom,
)}) translate(${toDomPrecision(-cameraX)}px, ${toDomPrecision(-cameraY)}px)`;Use position: absolute; in HTML layer, relative to the root element:
$htmlLayer.style.position = 'absolute';
$htmlLayer.style.top = topbarVisible ? `${TOP_NAVBAR_HEIGHT}px` : '0px';
$htmlLayer.style.left = '0px';HTML shape
In the External content sources example, we can see how tldraw supports HTML content:
class DangerousHtmlExample extends BaseBoxShapeUtil<IDangerousHtmlShape> {
static override type = 'html' as const;
override getDefaultProps() {
return {
type: 'html',
w: 500,
h: 300,
html: '<div>hello</div>',
};
}
}We also add a serializable shape. Besides the common x/y/width/height props, the most important attribute is the innerHTML content:
export interface HtmlAttributes {
html: string;
}
export interface HtmlSerializedNode
extends BaseSerializeNode<'html'>,
Partial<HtmlAttributes> {}When the position changes, we need to synchronize it via a CSS transform:
const { matrix } = entity.read(GlobalTransform);
$child.style.transform = `matrix(${toDomPrecision(
matrix.m00,
)}, ${toDomPrecision(matrix.m01)}, ${toDomPrecision(
matrix.m10,
)}, ${toDomPrecision(matrix.m11)}, ${toDomPrecision(
matrix.m20,
)}, ${toDomPrecision(matrix.m21)})`;
$child.style.width = `${toDomPrecision(width)}px`;
$child.style.height = `${toDomPrecision(height)}px`;Culling
In Lesson 8 - Culling, we discussed that HTML content entirely outside the viewport should be hidden, which can be achieved using display: none;. We use the method introduced in Lesson 18 - ECS to track all entities containing HTML components where the Culled component has changed, using System's query approach.
export class RenderHTML extends System {
private readonly culled = this.query(
(q) => q.with(HTML).addedChangedOrRemoved.with(Culled).trackWrites,
);
execute() {
this.culled.addedChangedOrRemoved.forEach((entity) => {
entity.read(HTMLContainer).element.style.display = entity.has(
Culled,
)
? 'none'
: 'block';
});
}
}But what if only part of it is outside the canvas? It is worth noting that tldraw sets the following CSS properties on the .tl-canvas container:
.tl-canvas {
overflow: clip;
content-visibility: auto;
touch-action: none;
contain: strict;
}| CSS property | Problem to solve |
|---|---|
| overflow: clip | Disable scrolling to ensure coordinate system stability and prevent scroll offset from corrupting rendering. |
| content-visibility: auto | Optimize the performance of DOM elements outside the viewport (such as selections, remote cursors, etc.) |
| touch-action: none | Completely take control of touch operations to avoid interference from the browser's default gestures. |
| contain: strict | Treat the canvas as an independent rendering island to reduce reflow and repaint overhead. |
Let's see how to display HTML content.
Paste URL
In Lesson 24 - Reading from clipboard, we covered how to handle images and text content from the clipboard.
URLs are special text. In tldraw:
- When the URL is recognized as an external link, the default handler fetches the page metadata (og:image, title, favicon, description), wraps it into a bookmark asset (TLBookmarkAsset) and the corresponding shape, and renders it with the bookmark style.
- When the URL is embeddable content (such as YouTube, Figma, Google Maps, etc.), it renders via an
<iframe>. - When the URL points to an image or video resource, it loads it as a media asset (TLImageAsset / TLVideoAsset) and renders it with ImageShapeUtil.
// @see https://github.com/tldraw/tldraw/blob/main/packages/tldraw/src/lib/ui/hooks/clipboard/pasteUrl.ts#L12
export async function pasteUrl() {
return await editor.putExternalContent({
type: 'url',
point,
url,
sources,
});
}Bookmark
// @see https://github.com/tldraw/tldraw/blob/ef0eba14c5a8baf4f36b3659ac9af98256d3b5dd/packages/tldraw/src/lib/defaultExternalContentHandlers.ts#L249
export async function defaultHandleExternalUrlAsset() {
let meta: {
image: string;
favicon: string;
title: string;
description: string;
};
const resp = await fetch(url, {
method: 'GET',
mode: 'no-cors',
});
const html = await resp.text();
const doc = new DOMParser().parseFromString(html, 'text/html');
meta = {
image:
doc.head
.querySelector('meta[property="og:image"]')
?.getAttribute('content') ?? '',
// title, favicon, description
};
// Create bookmark asset
}Render with iframe
Many websites provide sharing controls that embed content into web pages. Take YouTube as an example: you need to convert the playback link into an embeddable link using specific rules, after which you can display it using an <iframe>:
// Input URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=37fvFffAmf8
const embedUrl = `https://www.youtube.com/embed/${videoId}${search}`;
const $iframe = document.createElement('iframe');
$iframe.src = embedUrl;Image URL
Paste HTML content
Code blocks copied from VS Code are HTML fragments:
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<div
style="color: #e4e4e4;background-color: #181818;font-family: Menlo, Monaco, 'Courier New', monospace;font-weight: normal;font-size: 12px;line-height: 18px;white-space: pre;"
>
<div><span style="color: #d6d6dd;">### iframe</span></div>
</div>We can try reading it from the clipboard:
const html = event.clipboardData?.getData(MIME_TYPES.html); // text/htmlThen we can create the content based on the HTML. To get its size, insert the HTML into a hidden element and let the browser lay it out, then read its offsetWidth / offsetHeight.
function createHTML(
api: ExtendedAPI,
appState: AppState,
html: string,
position?: { x: number; y: number },
) {
const { width, height } = measureHTML(html);
updateAndSelectNodes(api, appState, [
{
id: uuidv4(),
type: 'html',
x: position?.x ?? 0,
y: position?.y ?? 0,
width,
height,
html,
},
]);
}Interact with HTML content
Some HTML content is interactive, such as embedding a YouTube player into the canvas while still allowing playback. However, setting pointer-events: none; on the HTML container prevents video playback. A common solution is to use a double-click interaction to enter edit mode, distinguishing it from the canvas's default single-click behavior for selecting shapes.
In fact, in Lesson 16 - Text input, we also used double-clicking a Text shape to enter edit mode. Here, we formally add an isEditing property to shapes.
export interface BaseSerializeNode<Type extends string> {
editable? boolean;
isEditing?: boolean;
}class RenderHTML extends System {
private readonly editables = this.query(
(q) => q.withAny(HTML, Embed).addedOrChanged.with(Editable).trackWrites,
);
execute() {
this.editables.addedOrChanged.forEach((entity) => {
const { element } = entity.read(HTMLContainer);
const { isEditing } = entity.read(Editable);
element.style.pointerEvents = isEditing ? 'auto' : 'none';
});
}
}Double-click the selected shape to enter edit mode. Click elsewhere to exit edit mode.
if (input.doubleClickTrigger) {
selection.mode = SelectionMode.EDITING;
api.updateNode(api.getNodeByEntity(selected), { isEditing: true });
}
if (input.pointerDownTrigger) {
if (selection.mode === SelectionMode.EDITING) {
const toSelect = this.getTopmostEntity(api, x, y, (e) => !e.has(UI));
if (selection.editing && toSelect !== selection.editing) {
api.updateNode(api.getNodeByEntity(selection.editing), {
isEditing: false,
});
selection.editing = undefined;
selection.mode = SelectionMode.SELECT;
}
}
}Double-click the YouTube player example above to enter edit mode, where you can play the video.
Export as SVG or Image
In Lesson 10 - Import and export images, we showed how to export the canvas content as SVG or PNG images. For HTML content you can rely on mature community solutions such as html-to-image.
This library uses a feature of SVG that allows having arbitrary HTML content inside of the <foreignObject> tag.